A Case on Child Employment
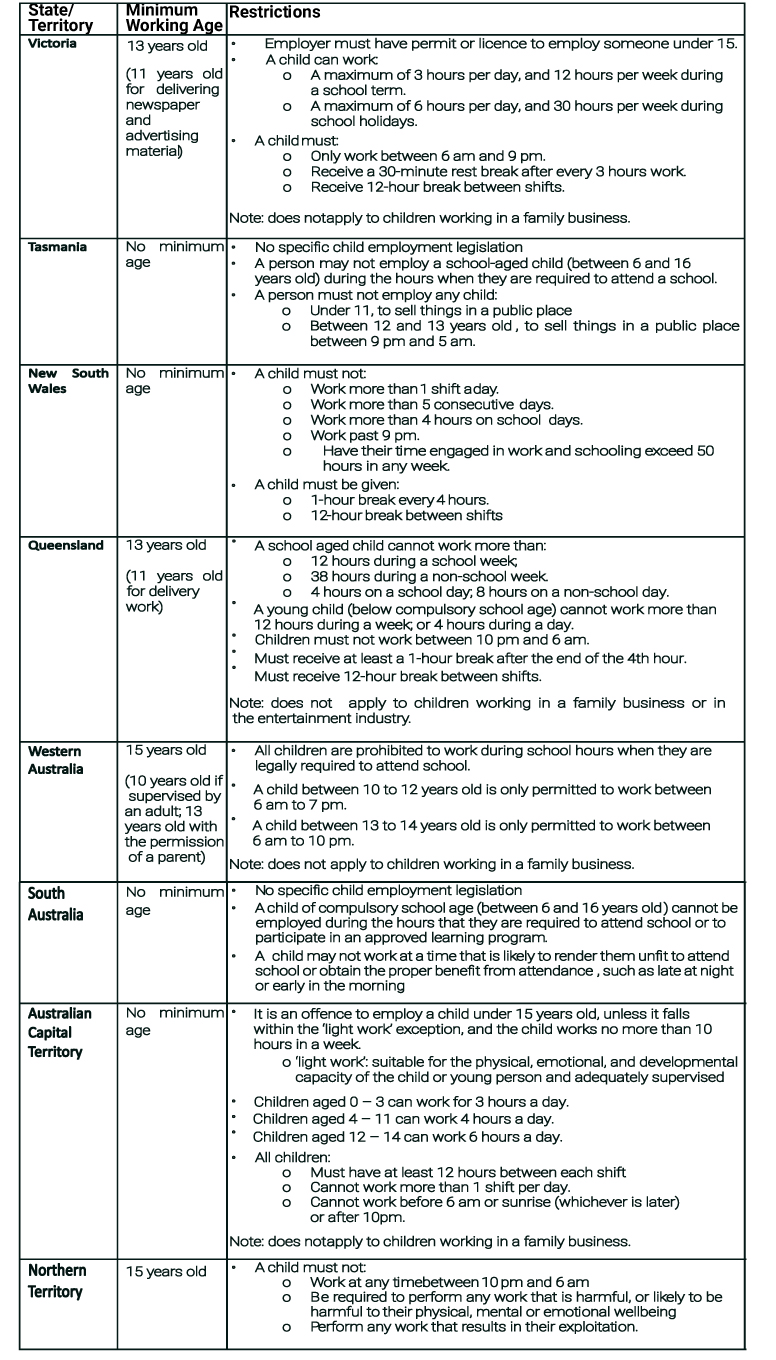
A recent Victorian case has highlighted the need for businesses engaging child employees to comply with their legal obligations.
Wage Inspectorate Victoria commenced proceedings against fashion retailer TK Maxx after discovering their Werribee store was employing a child without a permit. It warned TK Maxx Werribee that the child must cease work immediately, however TK Maxx employed another child without a permit the following week.
TK Maxx Werribee pleaded guilty to:
- Employing 2 children under 15 years of age without a permit
- Failing to ensure a child was supervised by someone with a Working with Children Check
- Employing a child for more hours than they were permitted to work
- Employing a child later than 9 pm
- Failing to provide children with a 30-minute rest break for every 3 hours worked
When considering penalties, the Court held that the offending was inadvertent and considered that TK Maxx had no prior offences, and had entered an early guilty plea.
This resulted in TK Maxx being placed on an adjourned undertaking for 12 months with a $5,000 penalty.